Electrical Steel Stators and Rotors
Electrical Steel Stators and Rotors – Precision Components for Medical and Industrial Motors
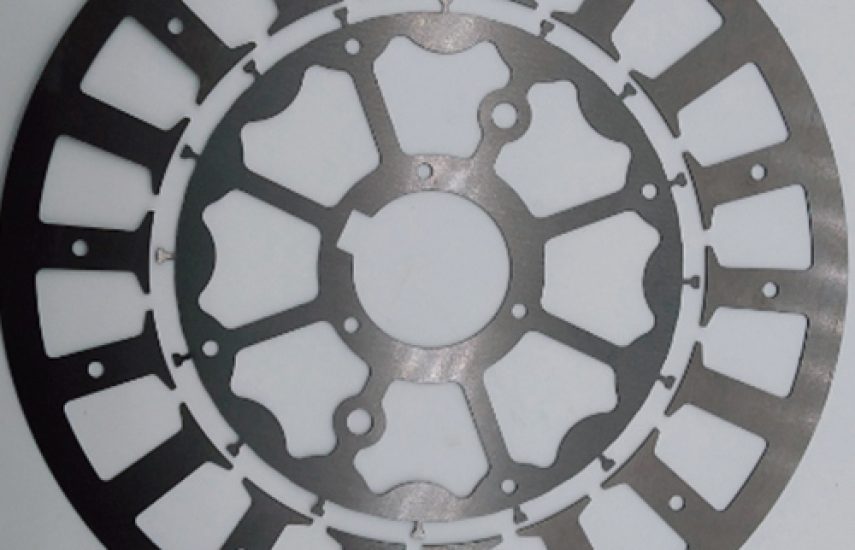
The Electrical Steel Stators and Rotors are high-precision laser-cut components designed for motors in medical devices and industrial applications. Manufactured using state-of-the-art five-axis laser cutting technology, these components deliver exceptional accuracy, durability, and a burr-free finish. Crafted from high-quality electrical steel (silicon steel, e.g., M19 or M36), they offer superior magnetic permeability and corrosion resistance, optimizing performance in MRI scanners, surgical robots, and industrial automation systems. The laser-cut design provides smooth surfaces and intricate laminated geometries, ensuring high electrical efficiency and reliability. Tailored for demanding environments, these components meet the rigorous standards of modern healthcare and industrial engineering, with recyclable materials supporting sustainable manufacturing.
Key Features:
- Ultra-Precise Cutting: Seam width of 15–30 µm with machining accuracy of ≤±10 µm for intricate motor designs.
- Burr-Free Finish: Smooth surfaces enhance performance and ensure safe integration in medical devices.
- High Magnetic Efficiency: Electrical steel (e.g., M19, M36) optimizes magnetic permeability for efficient motor operation.
- Corrosion Resistance: Engineered for durability in medical and industrial environments.
- Automated Production: Continuous feeding system ensures high efficiency and consistent quality.
- Customizable Design: Supports tailored lamination structures for specific motor requirements.
Certification and Standards:
Certified under ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 for quality management. Compliant with CE and FDA regulations for medical device safety and efficacy.
- High magnetic permeability (up to 2.2 T) optimizes energy conversion in motors and generators.
- Low core losses enhance efficiency and reduce energy waste in electrical systems.
- Magnetic softness ensures smooth and effective magnetic flux for reliable performance.
- Tensile strength of 270–400 MPa provides durability for demanding medical and industrial applications.
Electrical Steel (Silicon Steel)
An iron alloy with 0.8–4.8% silicon content, offering magnetic softness, low core losses, and high permeability (up to 2.2 T magnetic induction) for efficient energy conversion.
- Medical Devices: Essential for motors in MRI scanners, CT systems, and surgical robotic tools.
- Industrial Motors: Used in high-precision seromotors for automation, robotics, and conveyor systems.
- Diagnostic Equipment: Supports reliable motor components in advanced imaging and monitoring systems.
- Surgical Instruments: Incorporated in motors for minimally invasive surgical devices.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Used in the production of advanced motor-driven instruments.
- Material: Electrical Steel (Silicon Steel, e.g., M19, M36)
- Cutting Seam Width: 15–30 µm
- Machining Accuracy: ≤±10 µm
- Surface Roughness: Ra <0.2 µm
- Manufacturing Process: Five-axis laser cutting with automated feeding
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 300°C, suitable for sterilization
- Degradation: Non-degradable, designed for long-term stability