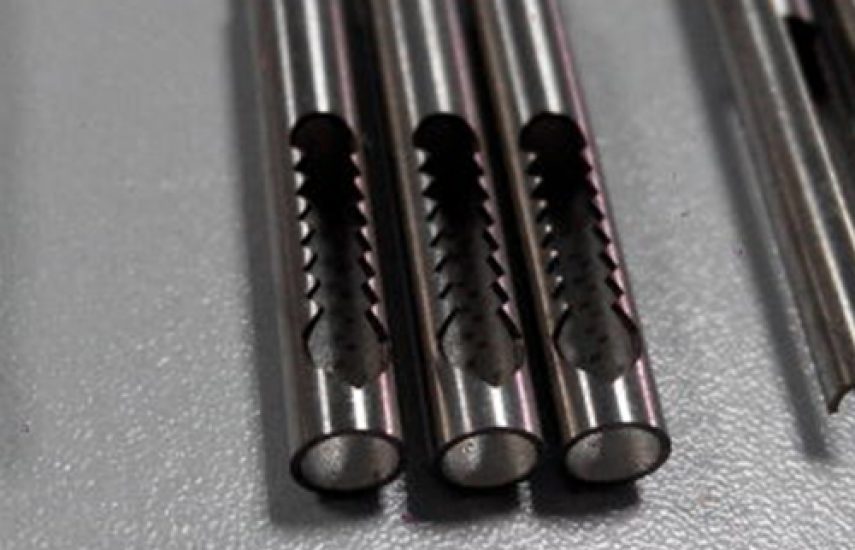
Surgical Stapler Tube
Stapler Tube – Precision Formed Tubes for Surgical Staplers
The Stapler Tube is a high-precision component designed for surgical staplers in medical applications. Manufactured using advanced five-axis laser cutting technology, this tube offers exceptional accuracy, durability, and a burr-free finish. Crafted from medical-grade materials such as stainless steel, Nitinol, or Cobalt-Chrome alloys, it ensures reliable performance in demanding surgical environments. The laser-formed tube features smooth surfaces and intricate geometries, minimizing tissue trauma and enhancing functionality in stapling procedures. Ideal for modern surgical staplers, this tube meets the rigorous demands of contemporary healthcare.
Key Features:
- High Precision: Seam width of 18–30 µm with machining accuracy of ≤±10 µm for intricate designs.
- Burr-Free Finish: Smooth edges ensure safe and effective surgical use.
- Material Versatility: Compatible with a range of high-performance alloys for diverse applications.
- High Durability: Engineered for wear resistance and long-term stability.
- Automated Production: Continuous feeding for high efficiency and consistent quality.
- Biocompatibility: Meets standards for safe medical use.
Certification and Standards:
Certified under ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and ISO 10993 for quality management and biocompatibility. Compliant with CE and FDA regulations for medical device safety and efficacy.
Stainless Steel SUS304:
Medical-grade SUS304 stainless steel (austenitic chromium-nickel alloy), offering excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
- Biocompatibility: Low risk of allergic reactions or toxicity, ideal for direct tissue contact in medical procedures.
- Mechanical Properties: High tensile strength (approximately 505 MPa) and elongation (up to 40%), providing flexibility without brittleness.
- Surface Finish: Laser-machined for smooth, burr-free edges, reducing the potential for tissue trauma or contamination.
- Thermal Stability: Maintains integrity across a wide temperature range, suitable for sterilization processes like autoclaving.
316L Stainless Steel:
316L Stainless Steel is a medical-grade austenitic chromium-nickel alloy renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. With a tensile strength of approximately 485–550 MPa and elongation up to 40%, it offers durability and flexibility without brittleness. Its low carbon content enhances weldability and resistance to intergranular corrosion, making it ideal for medical implants and instruments. Laser-machined for smooth, burr-free surfaces, it minimizes tissue irritation in sensitive applications.
Cobalt-Chromium Alloys (L605):
Cobalt-Chromium Alloys (L605) are medical-grade materials valued for their exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. With tensile strength ranging from 800–1500 MPa and hardness of 300–550 HV, they ensure durability in demanding medical applications. Ideal for implants and surgical tools, they support direct tissue contact with minimal reaction. Laser-machined surfaces provide smooth, burr-free finishes, enhancing performance in sensitive procedures.
Nickel-Titanium alloy:
Nitinol (NiTi), a nickel-titanium alloy, is renowned for its superelasticity and shape memory, making it a game-changer in medical applications. With a tensile strength of up to 1200 MPa and elastic modulus of 40–75 GPa, nitinol excels in demanding environments.
Cobalt-chrome alloy:
Cobalt-chrome (CoCr), an alloy of cobalt and chromium often enhanced with molybdenum, is prized for its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. With tensile strength ranging from 800–1500 MPa and hardness of 300–550 HV, CoCr is a cornerstone in medical technology. Popular grades like L605 (Co-Cr-W-Ni) and MP35N (Co-Cr-Ni-Mo) elevate its performance.
Aluminum alloy:
Aluminum Alloys are lightweight, medical-grade materials valued for their excellent corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio. With tensile strength typically ranging from 200–600 MPa and good ductility, they offer durability for medical and industrial applications. Their biocompatibility supports use in non-implantable devices and components. Laser-machined for smooth, burr-free surfaces, they minimize contamination risks and ensure compatibility with sterilization processes.
Magnesium alloy:
Magnesium, a lightweight (1.74 g/cm³) and biodegradable metal, is ideal for temporary medical implants like stents and orthopedic screws. Alloys such as WE43 or JDBM offer tensile strength (200–420 MPa) and controlled degradation (6–24 months), safely dissolving into non-toxic byproducts (Mg²⁺ ions). Its biocompatibility (ISO 10993) and ability to support tissue regeneration make it suitable for cardiovascular and bone repair applications. Magnesium’s elastic modulus closely matches bone, minimizing stress shielding in orthopedic uses.
- Surgical Staplers: Essential for forming tubes used in gastrointestinal, thoracic, and gynecological surgeries.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Supports precise stapling in laparoscopic and endoscopic operations.
- Orthopedic Surgery: Used in bone fixation and joint repair stapling devices.
- Cardiovascular Applications: Ideal for vascular stapling in advanced surgical techniques.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Incorporated in the production of high-precision stapling instruments.
- Material: 304 & 316L Stainless Steel, Ni-Ti Alloys, L605 Cobalt-Chromium, Aluminum, Magnesium
- Cutting Seam Width: 18–30 µm
- Machining Accuracy: ≤±10 µm
- Surface Roughness: Ra <0.2 µm
- Manufacturing Process: Five-axis laser cutting with automated feeding
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 300°C, suitable for sterilization
- Degradation: Non-degradable, designed for long-term stability